In October 2008 bitcoin released its whitepaper, it addressed a technology that was focused on creating a trustless system of electronic transactions, which includes decentralization and security, but little attention was paid to scalability. However, for a blockchain to function efficiently it should be able to provide solutions for decentralization, security, and scalability simultaneously. The inability to do this is the blockchain trilemma.
What is the blockchain trilemma?
A trilemma is a difficult choice from three options, each of which is unacceptable or unfavorable ~ Wikipedia
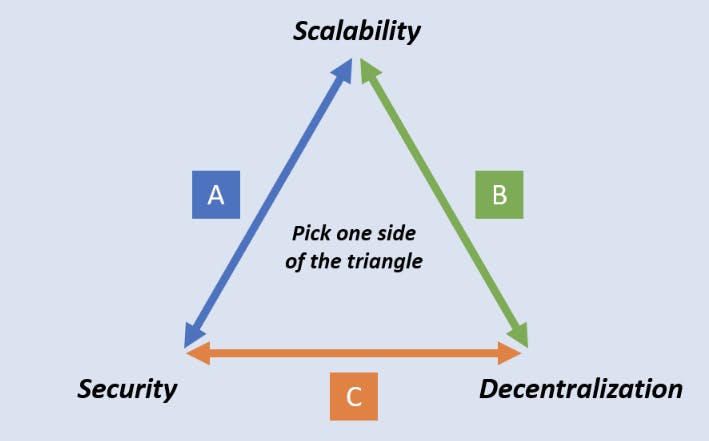
The blockchain trilemma is the challenge faced by developers when trying to build a blockchain network that is secure, scalable, and decentralized without picking one over the other.
The blockchain trilemma consists of three parameters;
Decentralization
This is the main interest of blockchain tech, the ability to distribute computing power and authority across every node in the blockchain network, thereby eliminating single entity authority.
Security
The ability of a blockchain to prevent bugs and external attacks.
Scalability
The ability of a blockchain to process more transactions as new users are being added to the network and to accommodate future growth when updates to the blockchain are due to be made.
Decentralization and security are non-negotiable for a blockchain network to thrive, this has made big blockchain projects like Bitcoin and Ethereum prioritize them both above scalability. On the other hand, private blockchains like Hyperlegder fabric are scalable and secure but centralized. Also, blockchain projects that have prioritized decentralization and scalability over security are usually targeted by hackers and malicious actors.
What is blockchain decentralization?
Decentralization is the backbone of blockchain technology; the transfer of authority and computing power from a single entity to a network of nodes (computers connected to the blockchain network). This single concept has brought about a revolution in the tech ecosystem.
Decentralization eliminates the need for a middleman or third party. Let's compare centralized and decentralized finance to solidify our understanding. When using a bank to make transactions, you must receive authentication and verification from the bank before the transaction reaches the intended recipient; occasionally, these transactions are turned down. Decentralized finance, on the other hand, offers financial tools without relying on middlemen exchanges or banks by using smart contracts on a blockchain, This makes transactions censorship resistant.
Nodes, rather than a single organization, carry out transaction authentication and verification in a decentralized network. This means that when a transaction is made and broadcast to a blockchain network, a majority of the computers connected to the network must come to an agreement (a consensus) to decide whether the transaction is valid or not. This process is known as "blockchain mining." As more miners attempt to validate transactions through consensus, the speed of transactions tends to slow down.
What is blockchain security?
As more nodes are added to the network, transactions would need to be validated by each member node, slowing down the network's pace but making it more safe and resistant to manipulation. The more decentralized a blockchain network is, the more secure it becomes.
On the other hand, blockchain networks that are centralized are more prone to manipulation and attacks as they have a limited number of nodes. Hackers frequently target networks like this, attempting to access more than 50% of their mining power. This is called a 51% attack.
What is blockchain scalability?
Scalability is the ability of the blockchain to accommodate large amounts of transactions and future growth. Although a blockchain network can be secure and decentralized, if it is not scalable, it will function poorly as more users adopt it, and adding future updates to the blockchain would cause its performance to suffer.
The only way blockchains can compete with centralized platforms is through scalability. For instance, while Visa handles about 1700 transactions per second, bitcoin processes only 4.6 transactions per second. Here, we can see that scalability is a constraint to the widespread use of blockchain technology.
Fortunately, scaling solutions and blockchains are being developed expressly to address the issue of transaction capacity, and progress is being made in overcoming blockchain's scaling limitations.
Conclusion
Understanding some of the concepts in this post may be difficult if you're new to web3. This is totally normal. I would encourage you to do some research and, if you can, reach out to people. You can also reach me on Twitter.
In the next article, I'll be addressing some of the blockchain scaling solutions, you can also drop questions in the comment section. I look forward to seeing you in the next article.